Helpful definitions of terms used for evaluating and treating infertility
Adverse Outcome
A pregnancy that does not result in a live birth. The adverse outcomes reported for ART procedures are miscarriages, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, induced abortions, and stillbirths.
American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM)
ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology)
All treatments or procedures that involve surgically removing eggs from a woman's ovaries and combining the eggs with sperm to help a woman become pregnant. The types of ART are in vitro fertilization, gamete intrafallopian transfer, and zygote intrafallopian transfer.
ART Cycle
A process in which 1) an ART procedure is carried out, 2) a woman has undergone ovarian stimulation or monitoring with the intent of having an ART procedure, or 3) frozen embryos have been thawed with the intent of transferring them to a woman. A cycle begins when a woman begins taking fertility drugs or having her ovaries monitored for follicle production.
Canceled Cycle
An ART cycle in which ovarian stimulation was carried out but which was stopped before eggs were retrieved, or in the case of frozen embryo cycles, before embryos were transferred.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
A government agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services responsible for publishing annual fertility clinic success rates.
Donor Egg Cycle
An embryo formed from the egg of one woman (the donor) and then transferred to another woman who is unable to conceive with her own eggs (the recipient). The donor relinquishes all parental rights to any resulting offspring.
Ectopic Pregnancy
A pregnancy in which the fertilized egg implants in a location outside of the uterus usually in the fallopian tube, the ovary, or the abdominal cavity. Ectopic pregnancy is a dangerous condition that must receive prompt treatment.
Egg
A female reproductive cell, also called an oocyte or ovum.
Egg Retrieval (also called oocyte retrieval)
A procedure to collect the eggs contained in the ovarian follicles.
Egg Transfer (also called oocyte transfer)
The transfer of retrieved eggs into a woman's fallopian tubes through laparoscopy (see definition). This procedure is used only in GIFT (see definition).
Embryo
An egg that has been fertilized by a sperm and undergone one or more divisions.
Embryo Transfer
Placement of embryos into a woman's uterus through the cervix after in vitro fertilization; in zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT) (see definition), the embryos are placed in a woman's fallopian tube.
Endometriosis
A medical condition involving the presence of tissue similar to the uterine lining in locations outside of the uterus, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and abdominal cavity.
Fecundity
The ability to conceive a pregnancy and carry it to term.
Fertility
The ability to conceive a pregnancy.
Fertilization
The penetration of the egg by the sperm and the resulting combining of genetic material that develops into an embryo.
Fetus
The unborn offspring from the eighth week after conception to the moment of birth.
Follicle
A structure in the ovaries that contains a developing egg.
Fresh Eggs, Sperm, or Embryos
Eggs, sperm, or embryos that have not been frozen. However, fresh embryos may have been conceived using fresh or frozen sperm.
Frozen Cycle
A cycle in which embryos are preserved through freezing (cryopreservation) for transfer at a later date.
Gamete
A reproductive cell, either a sperm or egg.
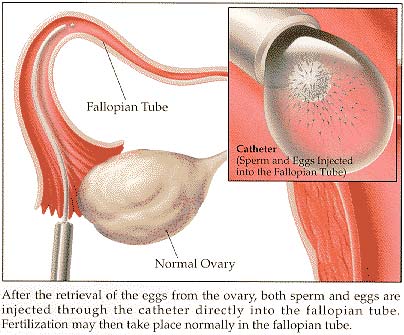
GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer)
An ART procedure that involves removing eggs from the woman's ovary, combining them with sperm, and using a laparoscope to place the unfertilized eggs and sperm into the woman's fallopian tube through small incisions in her abdomen.
Gestation
The period of time from conception to birth
Gestational Carrier (also called a gestational surrogate)
A woman who carries an embryo that was formed from the egg of another woman. The gestational carrier usually has a contractual obligation to return the infant to its intended parents.
Gestational Sac
A fluid-filled structure that develops within the uterus early in pregnancy. In a normal pregnancy, a gestational sac contains a developing fetus.
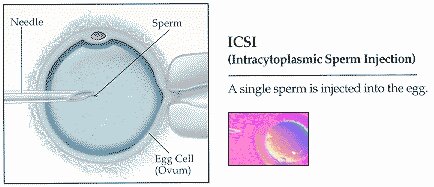
ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection)
A procedure in which a single sperm is injected directly into an egg; this procedure is most commonly used to overcome male infertility problems. Induced or therapeutic abortion A surgical or other medical procedure used to end a pregnancy.
Infertility
Difficulty achieving conception. In many studies, infertilty is defined as the failure of a couple to cenceive, despite unprotected intercourse, after a certain amount of time (usually 6 - 12 months).
Impared Fecundity
Difficulty conceiving or carrying a pregnancy to term, including situations in which pregnancy has been deemed medically risky for the woman and/or her offspring.
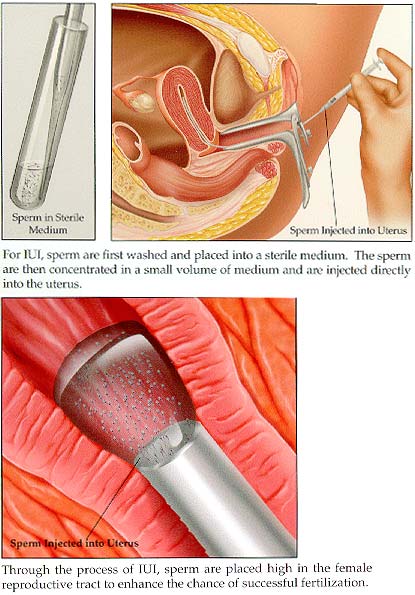
IUI (intrauterine insemination)
A medical procedure that involves placing sperm into a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization. IUI is not considered an ART procedure because it does not involve the manipulation of eggs.
IVF (in vitro fertilization)
An ART procedure that involves removing eggs from a woman's ovaries and fertilizing them outside her body. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the woman's uterus through the cervix.
Laparoscopy
A surgical procedure in which a fiber optic instrument (a laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to view the inside of the pelvis.
Live Birth
The delivery of one or more babies with any signs of life.
Male Factor
Any cause of infertility due to deficiencies in sperm quantity or that make it difficult for a sperm to fertilize an egg under normal conditions.
Miscarriage (also called spontaneous abortion)
A pregnancy ending in the spontaneous loss of the embryo or fetus before 20 weeks of gestation.
Multifetal Pregnancy Reduction
A procedure used to decrease the number of fetuses a woman carries and improve the chances that the remaining fetuses will develop into healthy infants. Multifetal reductions that occur naturally are referred to as spontaneous multifetal reductions.
Multiple Birth
A pregnancy that results in the birth of more than one infant.
Multiple Gestation
A pregnancy with multiple fetuses.
Oocyte
The female reproductive cell, also called an egg.
Ovarian Monitoring
The use of ultrasound and/or blood or urine tests to monitor follicle development and hormone production.
Ovarian Stimulation
The use of drugs to stimulate the ovaries to develop follicles and eggs.
Ovulatory Dysfunction
A cause of infertility due to problems with egg production by the ovaries.
Pregnancy (clinical)
Pregnancy documented by the presence of a gestational sac on ultrasound. For ART data collection purposes, pregnancy is defined as a clinical pregnancy rather than a chemical pregnancy (i.e., a positive pregnancy test).
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)
Genetic screening of embryos to detect deseases, improve IVF and gender selection success rates.
Primary Infertility
Infertility in persons who have never had children.
Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART)
An affiliate of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine composed of clinics and programs that provide ART. SART reports annual fertility clinic data to CDC.
Secondary Infertility
Infertility in persons who have already had children.
Singleton
A fetus which develops alone in the womb is called a singleton, in contrast, the general term for one offspring of a multiple birth is multiple.
Sperm
The male reproductive cell.
Sterility
Permanent infertility.
Stillbirth
An infant delivered without signs of life after 20 or more weeks of gestation.
Stimulated Cycle
An ART cycle in which a woman receives oral or injected fertility drugs to stimulate her ovaries to produce more follicles.
Surgical Sterility
Inability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term as a result of surgery. This catergory includes both the "contraceptively sterile," people who have sterilizing operations such as tubal ligation or vasectomy, and the "noncontraceptively sterile," people who are sterile as a result of surgery for other medical conditions (such as endometriosis, fibroid tumors or cancer).
Thawed Cycle
A cycle in which frozen embryos are thawed for transfer.
Tubal Factor
Structural or functional damage to one or both fallopian tubes that reduces fertility.
Ultrasound
A technique used in ART for visualizing the follicles in the ovaries and the gestational sac or fetus in the uterus.
Unstimulated Cycle
An ART cycle in which the woman does not receive drugs to stimulate her ovaries to produce more follicles. Instead, follicles develop naturally.
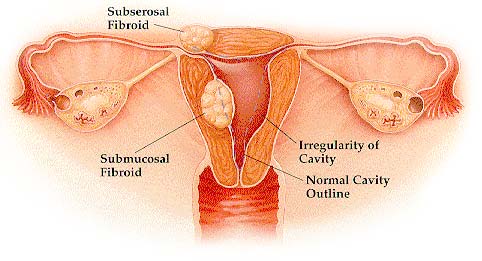
Uterine Factor
A disorder in the uterus (e.g., fibroid tumors) that reduces fertility.
ZIFT (zygote intrafallopian transfer)
An ART procedure in which eggs are collected from a woman's ovary and fertilized outside her body. A laparoscope is then used to place the resulting zygote (fertilized egg) into the woman's fallopian tube through a small incision in her abdomen.

